Abstract
Carbazoles are ubiquitous and privileged heterocyclic scaffolds in various functional organic materials and naturally occurring products. Although extensive efforts have focused on developing synthetic strategies toward carbazole derivatives, direct regioselective functionalization of the carbazole core remains challenging due to the inherently higher reactivity at the C3/C6 positions. In this study, we report a palladium-catalyzed, directing group-assisted, regioselective C1–H nitration of carbazoles. The protocol features a removable directing group and is amenable to gram-scale synthesis. This strategy provides a valuable platform for the selective functionalization of carbazoles, offering potential applications in optoelectronics, functional organic materials, and related areas while contributing to the advancement of C–H activation methodologies.
Graphical Abstract
Introduction
Carbazole represents an important heterocyclic scaffold that is broadly present in many natural products, biologically active motifs, as well as optoelectronic and functional materials [1-8]. By virtue of its substantial application in various fields, significant attention has been devoted to the chemical synthesis of carbazole and its derivatives [9-14]. To access substituted carbazole cores for pharmacophores and functional materials, two main synthetic routes are: i) sequential multistep syntheses of selectively substituted carbazoles and ii) functionalization of the carbazole core. Traditional approaches for constructing diversified carbazoles and derivatives are Fischer–Borsche synthesis [15,16], Graebe–Ullmann synthesis [17,18], cyclization of biaryl nitrenes–Cadogan synthesis [19], electrocyclic reactions [20,21], and others [22-24]. These methodologies are greatly limited due to harsh reaction conditions that impact the scope of the reaction, poor yield, and regioselectivity issues. In sharp contrast, transition metal-catalyzed cross-coupling reactions promisingly improve the regioselectivity issues and substrate scope [25-28]. In addition to cross-coupling reactions, transition metal-catalyzed cyclization involving C–H activation approaches have also been reported [29-36]. Despite the significant advances in carbazole core constructions, the established protocols significantly lack access to selectively C1-decorated carbazoles. Consequently, functionalizing carbazoles via transition metal-catalyzed directed C–H activation becomes more attractive to introduce the desired functionality in a regioselective fashion. The C–H activation strategy is elegant in many ways since it utilizes nonfunctionalized or lesser functionalized starting materials, reduces organometallic waste generation, has a broad substrate scope and a higher functional group compatibility, and features better resource- and step-economies [37-47]. In this context, several recent studies enabled the regioselective functionalization of carbazoles via C–H activation [48-61].
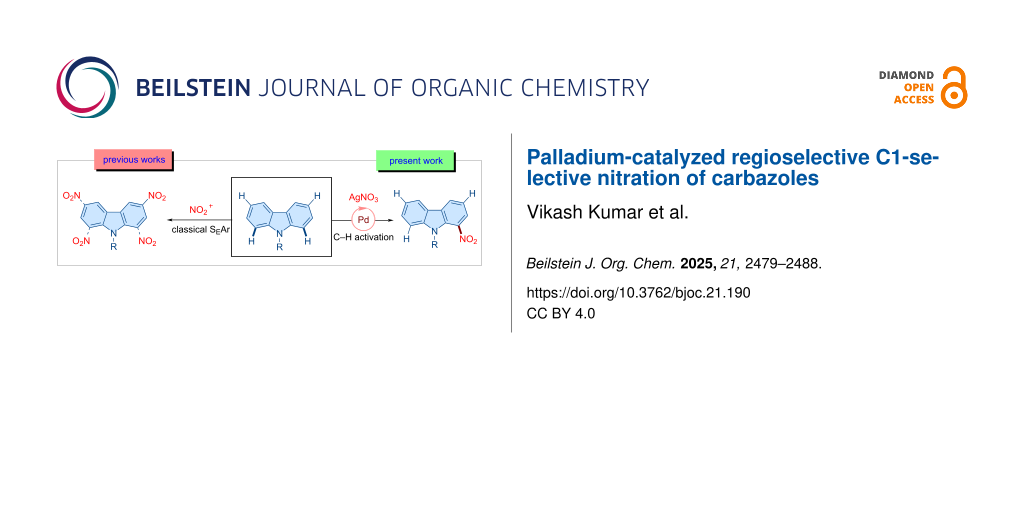
Among the variously substituted carbazole scaffolds, nitro-substituted carbazoles exhibit a diverse range of medicinal properties and serve as key starting materials for the synthesis of bioactive compounds and functional materials (Scheme 1a) [62-66]. Traditional electrophilic aromatic substitution methods for the nitration of carbazole typically result in a mixture of 1-nitro-, 2-nitro-, and 3-nitro-substituted isomers (Scheme 1b) [67]. Therefore, developing a method for the regioselective nitration of carbazole is highly desirable [68,69]. In this context, we envisioned utilizing a directing group-assisted regioselective C–H activation strategy to achieve the C1-selective nitration of carbazole. Through our efforts, we identified a palladium-catalyzed reaction system for C1 nitration of carbazole, which is presented in this study (Scheme 1c).
Scheme 1: (a) Representative examples of bioactive nitrocarbazoles. (b) Traditional electrophilic aromatic substitution approach for the nitration of carbazole. (c) Present work: palladium-catalyzed directed C1-selective nitration reaction.
Scheme 1: (a) Representative examples of bioactive nitrocarbazoles. (b) Traditional electrophilic aromatic su...
Results and Discussion
Optimization of the reaction parameters
To evaluate the feasibility of the reaction, we commenced our studies by exploring palladium-catalyzed regioselective ortho-C–H nitration of the N-pyridylcarbazole 1a as the model substrate, using silver nitrate as the nitrating agent (Table 1). After detailed optimization studies, we found that the treatment of 1a with AgNO3 in the presence of Pd2(dba)3 as the catalyst in 1,4-dioxane afforded the desired C1-nitrated product 2a in 69% isolated yield (Table 1, entry 1). Product 2a was thoroughly characterized by 1H and 13C NMR spectroscopy, HRMS, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis (Figure 1). A range of solvents was subsequently screened; however, none provided an improvement over 1,4-dioxane for this transformation (Table 1, entries 2 and 3). In addition to AgNO3, other silver and copper salts were examined as an oxidant to enhance the yield. Surprisingly, none of the tested silver salts afforded the desired product, while copper salts resulted in either trace amounts or a lower yield of 2a (Table 1, entries 4 and 5). We also evaluated inorganic oxidants, but these oxidants were ineffective in improving the reaction outcome (Table 1, entry 6). Other palladium complexes promoted the formation of 2a but with diminished efficiency (Table 1, entries 7 and 8). Varying the amount of AgNO3 did also not lead to a better yield (Table 1, entry 9), and alternative nitro sources also failed to enhance the product 2a yield (Table 1, entry 10). Attempts to optimize the reaction temperature did not yield improvements either (Table 1, entry 11). Control experiments confirmed that both the palladium catalyst and AgNO3 are essential for the reaction to proceed, as omission of either reagent resulted in complete loss of reactivity (Table 1, entry 12). Further, extending the reaction time had no significant effect on the yield (Table 1, entry 13). Finally, our investigation using various 3d transition metal catalysts such as Ni(OAc)2, Cu(OAc)2, and Co(OAc)2 in place of Pd₂(dba)3 did not lead to the formation of the desired product (Table 1, entry 14).
Table 1: Optimization studies.a
|
|
||
| entry | deviation from standard conditions | yield (%)b,c |
| 1 | no deviation | 69 |
| 2 | DCE/toluene/MeCN/GVL/cyrene | ND |
| 3 | THF/DMSO/MeOH/AcOH/DME | trace |
| 4d | 1.0 equiv AgOAc/Ag2O/Ag2CO3 | trace |
| 5d | 1.0 equiv CuOAc/Cu(OAc)2/Cu(OAc)2⋅H2O | 10/30/trace |
| 6d | 1.0 equiv K2S2O8/(NH4)2S2O8 | 57/33 |
| 7e | PdCl2/Pd(PPh3)2Cl2/Pd(PPh3)4/Pd(acac)2 | 25/24/(13)/(10) |
| 8e | Pd(dba)2/Pd(OAc)2 | (37)/34 |
| 9 | 1.5 equiv AgNO3 | 60 |
| 10f | 1.2 equiv FeNO3⋅9H2O/AgNO2/HNO3/t-BuNO2/iBuNO2 | 43/31/48/46/46 |
| 11 | 100/140 °C reaction temperature | 27/14 |
| 12 | without Pd2(dba)3 catalyst or AgNO3 | ND |
| 13 | reaction time 48 h | 69 |
| 14 | 1.0 equiv Ni(OAc)2 or Cu(OAc)2 or Co(OAc)2 in place of Pd2(dba)3 | ND |
aReaction conditions: 9-(pyridin-2-yl)-9H-carbazole (1a, 0.2 mmol, 1.0 equiv), Pd2(dba)3 (0.02 mmol, 10 mol %), AgNO3 (0.24 mmol, 1.2 equiv), and 1,4-dioxane (2.0 mL) at 120 °C for 24 h. ND = not detected. bYield of isolated product. cYield in parenthesis was determined by 1H NMR using mesitylene as internal standard. d1.0 equiv of oxidant was used along with AgNO3. e10 mol % of different palladium catalysts was used instead of Pd2(dba)3. f1.2 equiv of the different nitro sources used instead of AgNO3.
![[1860-5397-21-190-1]](/bjoc/content/figures/1860-5397-21-190-1.png?scale=2.0&max-width=1024&background=FFFFFF)
Figure 1: ORTEP diagram of compound 2a (CCDC 2478298).
Figure 1: ORTEP diagram of compound 2a (CCDC 2478298).
Building on the envisioned C1–H nitration of carbazoles, we further investigated the influence of various directing groups under the optimized reaction conditions (Scheme 2). Among the commonly employed directing groups tested, the 2-pyridyl group emerged as the most effective, enabling regioselective C1–H nitration to afford product 2a. Notably, control experiments using N-aryl-/N-alkyl-protected carbazoles and N-unsubstituted carbazole under standard conditions failed to produce the desired product.
Scheme 2: Effect of directing groups on the nitration of the carbazoles.
Scheme 2: Effect of directing groups on the nitration of the carbazoles.
Substrate scope
With the optimized reaction conditions in hand, we next explored the substrate scope (Scheme 3). The unsubstituted N-pyridylcarbazole 1a delivered the desired C1-nitrated product 2a in 69% yield. Carbazoles bearing 3,6-disubstitution (see 1j–l) participated smoothly, furnishing products 2j–l in good yield. The dibenzocarbazole derivative 1m underwent nitration to afford 2m in 55% yield. Likewise, 2-Ph-, 2-OMe-, and 2-Cl-substituted carbazoles were efficiently converted under the standard conditions, affording the corresponding C1 nitration products 2n–p in good yield, whereby C–H activation selectively occurred at the less hindered site. Halogenated substrates 1q and 1r (3-Cl and 3-Br substitution) delivered products 2q (37%) and 2r (31%) in moderate yield. Notably, the reaction of 1r also furnished 2a (9%), indicating competitive debromination. Finally, benzocarbazole substrate 1s afforded a mixture of regioisomers 2s (36%) and 2s' (15%). It is worth noting that under the standard reaction conditions, indole substrates 1t and 1u failed to afford the desired products 2t and 2u.
Scheme 3: Scope of the method. Reaction conditions: 1 (0.2 mmol, 1.0 equiv), Pd2(dba)3 (0.02 mmol, 10 mol %), AgNO3 (0.24 mmol, 1.2 equiv), and 1,4-dioxane (2.0 mL) at 120 °C for 24 h. a10 mol % of Pd(OAc)2 was used instead of Pd2(dba)3.
Scheme 3: Scope of the method. Reaction conditions: 1 (0.2 mmol, 1.0 equiv), Pd2(dba)3 (0.02 mmol, 10 mol %),...
Encouraged by these results, and to further demonstrate the synthetic utility of the established reaction protocol, we carried out a gram-scale synthesis under the optimized conditions. The reaction of 1a was performed on a 4.1 mmol (1.0 g) scale, yielding the C1–H-nitrated carbazole product 2a in 49% (0.585 g, 2.02 mmol) isolated yield (Scheme 4a). Given the importance of nitro-functionalized (hetero)arenes, we sought to access the NH-unsubstituted carbazole bearing a nitro group by removing the pyridyl directing group [58]. Treatment of compound 2a with methyl triflate, followed by hydrolysis with sodium hydroxide, successfully delivered the deprotected carbazole 3 in 53% yield (Scheme 4b).
Scheme 4: Gram-scale synthesis, directing group removal, and synthetic utility of our method.
Scheme 4: Gram-scale synthesis, directing group removal, and synthetic utility of our method.
Next, we demonstrated the reduction of the nitro group in compound 2a (Scheme 4c) [70-73]. Three distinct reaction conditions were found to be the most suitable to afford product 4 from 2a. Thus, the treatment of 2a with Sn/HCl gave 1-aminocarbazole derivative 4 in 88% yield. Furthermore, the reduction was also achieved using NiCl2/NaBH4 in methanol at room temperature, affording the corresponding amine 4 in 93% yield. To align with green chemistry principles, we employed a recently reported mechanochemical protocol by Ito and co-workers for the reduction of nitro compounds to amines [72]. Using this solvent-free method, compound 2a was successfully reduced to the corresponding amine 4 in 85% yield. Similarly, the nitro group of compound 3 was also reduced under the NiCl2/NaBH4-promoted conditions, affording 9H-carbazol-1-amine (5) in 90% yield.
Mechanistic studies
Next, we sought to gain mechanistic insights into the catalytic pathway through a series of experiments (Scheme 5). To probe the nature of the C–H activation step, the reaction was conducted in fully deuterated methanol as both cosolvent and solvent (Scheme 5a). No H/D scrambling was observed at the C1 position of the recovered starting material 1a, suggesting that the cyclopalladation step is irreversible. To further investigate the nature of the C–H activation step, an intramolecular kinetic isotope effect (KIE) experiment was performed using monodeuterated substrate 1a-D1. A modest KIE value of kH/kD = 1.5 was observed under standard reaction conditions after 2 hours, indicating that C–H bond cleavage is kinetically relevant and likely involved in the rate-determining step (Scheme 5b). To gain additional mechanistic insight, we synthesized palladacycle intermediate 6 following the reported procedure [58]. Then, the reaction was carried out using palladacycle 6 as the catalyst, and the desired nitrated product 2a was obtained in 48% yield (Scheme 5c). This result supports the involvement of palladacycle intermediate 6 in the catalytic cycle.
Proposed mechanism
Based on our experimental results and related literature precedents [68,69,74-80], a plausible catalytic cycle is proposed (Figure 2). The catalytic cycle commences with the formation of active palladium(II) species 7 in the presence of AgNO3. Coordination of the pyridyl group of 1a to Pd(NO₃)₂ is followed by irreversible C–H bond cleavage via cyclopalladation to form a six-membered palladacycle intermediate 9. Subsequent reaction with in situ-generated HNO3 facilitates nitro group incorporation to form the C1-nitrated carbazole product 2a and regeneration of the active palladium catalyst 7, thereby completing the catalytic cycle.
Conclusion
In summary, we have developed a regioselective protocol for the direct C1–H nitration of carbazoles, an important class of heterocycles with wide-ranging applications in materials science and natural products chemistry. The transformation proceeds using commercially available Pd2(dba)3 as the catalyst and silver nitrate as the nitro source. The catalytic system demonstrates a satisfactory substrate scope and excellent regioselectivity. The scalability of the reaction was demonstrated, further underscoring the robustness of the protocol. Overall, this study highlights the potential of palladium-catalyzed C–H activation strategies in streamlining access to nitro-functionalized carbazoles for applications in organic synthesis and materials science.
Experimental
A 15 mL pressure tube was charged with Pd2(dba)3 (18.3 mg, 0.02 mmol, 10 mol %), N-(pyridin-2-yl)-9H-carbazole 1 (0.2 mmol, 1.0 equiv), and AgNO3 (41 mg, 0.24 mmol, 1.2 equiv). Then, the solvent 1,4-dioxane (2.0 mL) was added, and the reaction mixture was allowed to stir in a preheated oil bath at 120 °C for 24 h. Upon completion of the reaction time, the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature and diluted with dichloromethane (10 mL). The reaction mixture was filtered through a Celite pad, and the filtrate was concentrated using a rotary evaporator. The crude residue was purified through silica gel column chromatography using n-hexane/EtOAc 99:1 as eluent to give the pure C1-nitrated carbazole 2.
Supporting Information
| Supporting Information File 1: Experiment details, characterization data, copy of NMR spectra of synthesized compounds, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction data. | ||
| Format: PDF | Size: 5.0 MB | Download |
| Supporting Information File 2: CIF file for 2a. | ||
| Format: CIF | Size: 386.7 KB | Download |
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the Indian Institute of Technology Tirupati for the infrastructure and instrumentation facilities.
Funding
We are grateful to the Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF) of India (Grant No. CRG/2023/008708) and the Ministry of Education (MoE) of India (Grant No. MoE-STARS/STARS-2/2023-0685) for the financial support. The authors also thank the Indian Institute of Technology Tirupati for providing infrastructure, facilities, and fellowship to V.K. and C.V.
Data Availability Statement
All data that supports the findings of this study is available in the published article and/or the supporting information of this article.
References
-
Caruso, A.; Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Saturnino, C.; Mauro, M. V.; Bruno, R.; Aquaro, S.; Sinicropi, M. S. Molecules 2019, 24, 1912. doi:10.3390/molecules24101912
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Issa, S.; Prandina, A.; Bedel, N.; Rongved, P.; Yous, S.; Le Borgne, M.; Bouaziz, Z. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1321–1346. doi:10.1080/14756366.2019.1640692
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Głuszyńska, A. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 94, 405–426. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.02.059
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Jiang, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 2014–2025. doi:10.2174/138527212803251604
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Karon, K.; Lapkowski, M. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 2601–2610. doi:10.1007/s10008-015-2973-x
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Manickam, M.; Iqbal, P.; Belloni, M.; Kumar, S.; Preece, J. A. Isr. J. Chem. 2012, 52, 917–934. doi:10.1002/ijch.201200058
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Tsutsumi, L. S.; Gündisch, D.; Sun, D. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1290–1313. doi:10.2174/1568026615666150915112647
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Bedford, R. B.; Cazin, C. S. J. Chem. Commun. 2002, 2310–2311. doi:10.1039/b207712b
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Afrin, A.; Chinna Ayya Swamy, P. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 1923–1944. doi:10.1039/d3tc04121b
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Allen, L. A. T.; Natho, P. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023, 21, 8956–8974. doi:10.1039/d3ob01605f
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Schmidt, A. W.; Reddy, K. R.; Knölker, H.-J. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3193–3328. doi:10.1021/cr200447s
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Xu, Z.; Wu, D.; Fang, C.; Li, Y. Des. Monomers Polym. 2023, 26, 90–105. doi:10.1080/15685551.2023.2194174
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Aggarwal, T.; Sushmita, S.; Verma, A. K. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 8330–8342. doi:10.1039/c9ob01381d
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Konidena, R. K.; Thomas, K. R. J.; Park, J. W. ChemPhotoChem 2022, 6, e202200059. doi:10.1002/cptc.202200059
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Borsche, W. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1908, 359, 49–80. doi:10.1002/jlac.19083590103
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Fischer, E.; Jourdan, F. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1883, 16, 2241–2245. doi:10.1002/cber.188301602141
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Ullmann, F. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1904, 332, 82–104. doi:10.1002/jlac.19043320105
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Graebe, C.; Ullmann, F. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1896, 291, 16–17. doi:10.1002/jlac.18962910104
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Cadogan, J. I. G.; Cameron-Wood, M.; Mackie, R. K.; Searle, R. J. G. J. Chem. Soc. 1965, 4831–4837. doi:10.1039/jr9650004831
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Kano, S.; Sugino, E.; Shibuya, S.; Hibino, S. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 3856–3859. doi:10.1021/jo00332a019
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Hibino, S.; Tonari, A.; Choshi, T.; Sugino, E. Heterocycles 1993, 35, 441–444. doi:10.3987/com-92-s54
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Freeman, A. W.; Urvoy, M.; Criswell, M. E. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 5014–5019. doi:10.1021/jo0503299
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Sanz, R.; Escribano, J.; Pedrosa, M. R.; Aguado, R.; Arnáiz, F. J. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 713–718. doi:10.1002/adsc.200600384
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Smitrovich, J. H.; Davies, I. W. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 533–535. doi:10.1021/ol036294l
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Liu, Z.; Larock, R. C. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 347–355. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2006.10.071
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Kitawaki, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Ueno, A.; Chida, N. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 6792–6801. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2006.04.087
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Liu, Z.; Larock, R. C. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3739–3741. doi:10.1021/ol048564l
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Nozaki, K.; Takahashi, K.; Nakano, K.; Hiyama, T.; Tang, H.-Z.; Fujiki, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Tamao, K. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2051–2053. doi:10.1002/anie.200250648
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Liégault, B.; Lee, D.; Huestis, M. P.; Stuart, D. R.; Fagnou, K. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 5022–5028. doi:10.1021/jo800596m
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Jordan-Hore, J. A.; Johansson, C. C. C.; Gulias, M.; Beck, E. M.; Gaunt, M. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16184–16186. doi:10.1021/ja806543s
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Ackermann, L.; Althammer, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1627–1629. doi:10.1002/anie.200603833
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Akermark, B.; Eberson, L.; Jonsson, E.; Pettersson, E. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 1365–1367. doi:10.1021/jo00897a048
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Suzuki, C.; Hirano, K.; Satoh, T.; Miura, M. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1597–1600. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00502
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Cho, S. H.; Yoon, J.; Chang, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5996–6005. doi:10.1021/ja111652v
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Bjørsvik, H.-R.; Elumalai, V. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 5474–5479. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201601191
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Ackermann, L.; Althammer, A.; Mayer, P. Synthesis 2009, 3493–3503. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1216977
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Sinha, S. K.; Guin, S.; Maiti, S.; Biswas, J. P.; Porey, S.; Maiti, D. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5682–5841. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00220
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Rej, S.; Ano, Y.; Chatani, N. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1788–1887. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00495
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Gandeepan, P.; Müller, T.; Zell, D.; Cera, G.; Warratz, S.; Ackermann, L. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2192–2452. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00507
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Murakami, K.; Yamada, S.; Kaneda, T.; Itami, K. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9302–9332. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00021
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Liu, C.-X.; Yin, S.-Y.; Zhao, F.; Yang, H.; Feng, Z.; Gu, Q.; You, S.-L. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 10079–10134. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00149
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Josephitis, C. M.; Nguyen, H. M. H.; McNally, A. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 7655–7691. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00881
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Docherty, J. H.; Lister, T. M.; Mcarthur, G.; Findlay, M. T.; Domingo-Legarda, P.; Kenyon, J.; Choudhary, S.; Larrosa, I. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 7692–7760. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00888
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Crabtree, R. H.; Lei, A. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8481–8482. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00307
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Giri, R.; Shi, B.-F.; Engle, K. M.; Maugel, N.; Yu, J.-Q. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3242–3272. doi:10.1039/b816707a
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Wencel-Delord, J.; Dröge, T.; Liu, F.; Glorius, F. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4740–4761. doi:10.1039/c1cs15083a
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Baudoin, O. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4902–4911. doi:10.1039/c1cs15058h
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Kumar, V.; Sudharsan, S.; Mantry, L.; Maayuri, R.; Das, M.; Gandeepan, P. Chem. Rec. 2025, 25, e202500042. doi:10.1002/tcr.202500042
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Elsaid, M.; Ge, R.; Liu, C.; Maiti, D.; Ge, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303110. doi:10.1002/anie.202303110
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Rzayev, J.; Zhang, Z.; Durand, N.; Soulé, J.-F. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 6755–6760. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.2c02514
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Cho, E. H.; Akhtar, M. S.; Aslam, M.; Thombal, R. S.; Li, X.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, Y. R. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 6776–6783. doi:10.1039/d2ob01077a
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Zhang, L.; Zhao, R.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Niu, J.-L.; Yang, H.-R.; Gao, L.; Liu, S.-L.; Zhou, L. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2023, 365, 3461–3466. doi:10.1002/adsc.202300677
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Rajat; Jain, N. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 8600–8608. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.3c00511
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Shahid, M.; Punnya, A. J.; Babu, S. S.; Sarkar, S.; Gopinath, P. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 13686–13698. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.3c01350
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Maiti, S.; Mandal, T.; Dash, B. P.; Dash, J. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 1396–1407. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.0c01746
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Chu, J.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Chang, D.-H.; Lee, Y.-M.; Wu, M.-J. Organometallics 2013, 32, 272–282. doi:10.1021/om301071m
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Shahid, M.; Muthuraja, P.; Gopinath, P. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 753–758. doi:10.1039/d3ob01827j
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Dharaniyedath, J.; Kumar, V.; Gandeepan, P. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 27, e202400649. doi:10.1002/ejoc.202400649
Return to citation in text: [1] [2] [3] -
Banerjee, S.; De, P. B.; Pradhan, S.; Shah, T. A.; Punniyamurthy, T. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 1677–1684. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201801829
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Qiu, R.; Reddy, V. P.; Iwasaki, T.; Kambe, N. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 367–374. doi:10.1021/jo502402d
Return to citation in text: [1] -
De, P. B.; Banerjee, S.; Pradhan, S.; Punniyamurthy, T. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 5889–5898. doi:10.1039/c8ob01603h
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Santos, H.; Zeoly, L. A.; Rebechi, R.; Arantes, J.; Coelho, F.; Rodrigues, M. T., Jr. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2024, 366, 884–891. doi:10.1002/adsc.202301328
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Singh, S.; Samineni, R.; Pabbaraja, S.; Mehta, G. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 3372–3376. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01111
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Sinicropi, M. S.; Tavani, C.; Rosano, C.; Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Barbarossa, A.; Bianchi, L.; Benzi, A.; Maccagno, M.; Ponassi, M.; Spinelli, D.; Petrillo, G. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9139. doi:10.3390/app11199139
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Kim, M.; Jeon, S. K.; Hwang, S.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Yu, E.; Lee, J. Y. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 2485–2493. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b09114
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Fan, Z.; Ni, J.; Zhang, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8470–8475. doi:10.1021/jacs.6b03402
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Kyziol, J. B.; Daszkiewicz, Z. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 1857–1861. doi:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)91140-8
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Qian, Y.-E.; Zheng, L.; Xiang, H.-Y.; Yang, H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 4835–4851. doi:10.1039/d1ob00384d
Return to citation in text: [1] [2] -
Song, L.-R.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, A. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 1351–1361. doi:10.1039/c8ob02750a
Return to citation in text: [1] [2] -
Campbell, C. D.; Stewart, M. I. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 3171–3178. doi:10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00283
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Dinér, P.; Proietti, G.; Prathap, K. J.; Ye, X.; Olsson, R. T. Synthesis 2022, 54, 133–146. doi:10.1055/a-1579-2190
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Kubota, K.; Nagao, A.; Ito, H. RSC Mechanochem. 2025, 2, 389–393. doi:10.1039/d4mr00138a
Return to citation in text: [1] [2] -
Patrick, D. A.; Gillespie, J. R.; McQueen, J.; Hulverson, M. A.; Ranade, R. M.; Creason, S. A.; Herbst, Z. M.; Gelb, M. H.; Buckner, F. S.; Tidwell, R. R. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 957–971. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01163
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Jiang, G. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9589–9592. doi:10.1039/c6cc04341k
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Jeong, T.; Han, S. H.; Han, S.; Sharma, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J. S.; Kwak, J. H.; Jung, Y. H.; Kim, I. S. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 232–235. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b03368
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Sharma, S.; Han, S. H.; Han, S.; Ji, W.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Oh, J. S.; Jung, Y. H.; Kim, I. S. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2852–2855. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b01298
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Han, S.; Mishra, N. K.; Sharma, S.; Park, J.; Choi, M.; Lee, S.-Y.; Oh, J. S.; Jung, Y. H.; Kim, I. S. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 8026–8035. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.5b01149
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Muralirajan, K.; Cheng, C.-H. Chem. – Eur. J. 2013, 19, 6198–6202. doi:10.1002/chem.201300922
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Lian, Y.; Hummel, J. R.; Bergman, R. G.; Ellman, J. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12548–12551. doi:10.1021/ja406131a
Return to citation in text: [1] -
Lian, Y.; Bergman, R. G.; Lavis, L. D.; Ellman, J. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7122–7125. doi:10.1021/ja402761p
Return to citation in text: [1]
| 68. | Qian, Y.-E.; Zheng, L.; Xiang, H.-Y.; Yang, H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 4835–4851. doi:10.1039/d1ob00384d |
| 69. | Song, L.-R.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, A. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 1351–1361. doi:10.1039/c8ob02750a |
| 74. | Li, J.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Yang, H.; Jiang, G. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 9589–9592. doi:10.1039/c6cc04341k |
| 75. | Jeong, T.; Han, S. H.; Han, S.; Sharma, S.; Park, J.; Lee, J. S.; Kwak, J. H.; Jung, Y. H.; Kim, I. S. Org. Lett. 2016, 18, 232–235. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b03368 |
| 76. | Sharma, S.; Han, S. H.; Han, S.; Ji, W.; Oh, J.; Lee, S.-Y.; Oh, J. S.; Jung, Y. H.; Kim, I. S. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 2852–2855. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b01298 |
| 77. | Han, S.; Mishra, N. K.; Sharma, S.; Park, J.; Choi, M.; Lee, S.-Y.; Oh, J. S.; Jung, Y. H.; Kim, I. S. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 8026–8035. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.5b01149 |
| 78. | Muralirajan, K.; Cheng, C.-H. Chem. – Eur. J. 2013, 19, 6198–6202. doi:10.1002/chem.201300922 |
| 79. | Lian, Y.; Hummel, J. R.; Bergman, R. G.; Ellman, J. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 12548–12551. doi:10.1021/ja406131a |
| 80. | Lian, Y.; Bergman, R. G.; Lavis, L. D.; Ellman, J. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7122–7125. doi:10.1021/ja402761p |
| 72. | Kubota, K.; Nagao, A.; Ito, H. RSC Mechanochem. 2025, 2, 389–393. doi:10.1039/d4mr00138a |
| 58. | Dharaniyedath, J.; Kumar, V.; Gandeepan, P. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 27, e202400649. doi:10.1002/ejoc.202400649 |
| 1. | Caruso, A.; Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Saturnino, C.; Mauro, M. V.; Bruno, R.; Aquaro, S.; Sinicropi, M. S. Molecules 2019, 24, 1912. doi:10.3390/molecules24101912 |
| 2. | Issa, S.; Prandina, A.; Bedel, N.; Rongved, P.; Yous, S.; Le Borgne, M.; Bouaziz, Z. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 1321–1346. doi:10.1080/14756366.2019.1640692 |
| 3. | Głuszyńska, A. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 94, 405–426. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.02.059 |
| 4. | Jiang, H.; Sun, J.; Zhang, J. Curr. Org. Chem. 2012, 16, 2014–2025. doi:10.2174/138527212803251604 |
| 5. | Karon, K.; Lapkowski, M. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2015, 19, 2601–2610. doi:10.1007/s10008-015-2973-x |
| 6. | Manickam, M.; Iqbal, P.; Belloni, M.; Kumar, S.; Preece, J. A. Isr. J. Chem. 2012, 52, 917–934. doi:10.1002/ijch.201200058 |
| 7. | Tsutsumi, L. S.; Gündisch, D.; Sun, D. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1290–1313. doi:10.2174/1568026615666150915112647 |
| 8. | Bedford, R. B.; Cazin, C. S. J. Chem. Commun. 2002, 2310–2311. doi:10.1039/b207712b |
| 19. | Cadogan, J. I. G.; Cameron-Wood, M.; Mackie, R. K.; Searle, R. J. G. J. Chem. Soc. 1965, 4831–4837. doi:10.1039/jr9650004831 |
| 58. | Dharaniyedath, J.; Kumar, V.; Gandeepan, P. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 27, e202400649. doi:10.1002/ejoc.202400649 |
| 17. | Ullmann, F. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1904, 332, 82–104. doi:10.1002/jlac.19043320105 |
| 18. | Graebe, C.; Ullmann, F. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1896, 291, 16–17. doi:10.1002/jlac.18962910104 |
| 70. | Campbell, C. D.; Stewart, M. I. J. Chem. Educ. 2023, 100, 3171–3178. doi:10.1021/acs.jchemed.3c00283 |
| 71. | Dinér, P.; Proietti, G.; Prathap, K. J.; Ye, X.; Olsson, R. T. Synthesis 2022, 54, 133–146. doi:10.1055/a-1579-2190 |
| 72. | Kubota, K.; Nagao, A.; Ito, H. RSC Mechanochem. 2025, 2, 389–393. doi:10.1039/d4mr00138a |
| 73. | Patrick, D. A.; Gillespie, J. R.; McQueen, J.; Hulverson, M. A.; Ranade, R. M.; Creason, S. A.; Herbst, Z. M.; Gelb, M. H.; Buckner, F. S.; Tidwell, R. R. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 957–971. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01163 |
| 15. | Borsche, W. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1908, 359, 49–80. doi:10.1002/jlac.19083590103 |
| 16. | Fischer, E.; Jourdan, F. Ber. Dtsch. Chem. Ges. 1883, 16, 2241–2245. doi:10.1002/cber.188301602141 |
| 67. | Kyziol, J. B.; Daszkiewicz, Z. Tetrahedron 1984, 40, 1857–1861. doi:10.1016/s0040-4020(01)91140-8 |
| 9. | Afrin, A.; Chinna Ayya Swamy, P. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 1923–1944. doi:10.1039/d3tc04121b |
| 10. | Allen, L. A. T.; Natho, P. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2023, 21, 8956–8974. doi:10.1039/d3ob01605f |
| 11. | Schmidt, A. W.; Reddy, K. R.; Knölker, H.-J. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 3193–3328. doi:10.1021/cr200447s |
| 12. | Xu, Z.; Wu, D.; Fang, C.; Li, Y. Des. Monomers Polym. 2023, 26, 90–105. doi:10.1080/15685551.2023.2194174 |
| 13. | Aggarwal, T.; Sushmita, S.; Verma, A. K. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 8330–8342. doi:10.1039/c9ob01381d |
| 14. | Konidena, R. K.; Thomas, K. R. J.; Park, J. W. ChemPhotoChem 2022, 6, e202200059. doi:10.1002/cptc.202200059 |
| 68. | Qian, Y.-E.; Zheng, L.; Xiang, H.-Y.; Yang, H. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2021, 19, 4835–4851. doi:10.1039/d1ob00384d |
| 69. | Song, L.-R.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, A. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2019, 17, 1351–1361. doi:10.1039/c8ob02750a |
| 29. | Liégault, B.; Lee, D.; Huestis, M. P.; Stuart, D. R.; Fagnou, K. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 5022–5028. doi:10.1021/jo800596m |
| 30. | Jordan-Hore, J. A.; Johansson, C. C. C.; Gulias, M.; Beck, E. M.; Gaunt, M. J. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 16184–16186. doi:10.1021/ja806543s |
| 31. | Ackermann, L.; Althammer, A. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 1627–1629. doi:10.1002/anie.200603833 |
| 32. | Akermark, B.; Eberson, L.; Jonsson, E.; Pettersson, E. J. Org. Chem. 1975, 40, 1365–1367. doi:10.1021/jo00897a048 |
| 33. | Suzuki, C.; Hirano, K.; Satoh, T.; Miura, M. Org. Lett. 2015, 17, 1597–1600. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.5b00502 |
| 34. | Cho, S. H.; Yoon, J.; Chang, S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 5996–6005. doi:10.1021/ja111652v |
| 35. | Bjørsvik, H.-R.; Elumalai, V. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2016, 5474–5479. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201601191 |
| 36. | Ackermann, L.; Althammer, A.; Mayer, P. Synthesis 2009, 3493–3503. doi:10.1055/s-0029-1216977 |
| 48. | Kumar, V.; Sudharsan, S.; Mantry, L.; Maayuri, R.; Das, M.; Gandeepan, P. Chem. Rec. 2025, 25, e202500042. doi:10.1002/tcr.202500042 |
| 49. | Elsaid, M.; Ge, R.; Liu, C.; Maiti, D.; Ge, H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303110. doi:10.1002/anie.202303110 |
| 50. | Rzayev, J.; Zhang, Z.; Durand, N.; Soulé, J.-F. Org. Lett. 2022, 24, 6755–6760. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.2c02514 |
| 51. | Cho, E. H.; Akhtar, M. S.; Aslam, M.; Thombal, R. S.; Li, X.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, Y. R. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2022, 20, 6776–6783. doi:10.1039/d2ob01077a |
| 52. | Zhang, L.; Zhao, R.; Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Niu, J.-L.; Yang, H.-R.; Gao, L.; Liu, S.-L.; Zhou, L. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2023, 365, 3461–3466. doi:10.1002/adsc.202300677 |
| 53. | Rajat; Jain, N. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 8600–8608. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.3c00511 |
| 54. | Shahid, M.; Punnya, A. J.; Babu, S. S.; Sarkar, S.; Gopinath, P. J. Org. Chem. 2023, 88, 13686–13698. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.3c01350 |
| 55. | Maiti, S.; Mandal, T.; Dash, B. P.; Dash, J. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 86, 1396–1407. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.0c01746 |
| 56. | Chu, J.-H.; Wu, C.-C.; Chang, D.-H.; Lee, Y.-M.; Wu, M.-J. Organometallics 2013, 32, 272–282. doi:10.1021/om301071m |
| 57. | Shahid, M.; Muthuraja, P.; Gopinath, P. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2024, 22, 753–758. doi:10.1039/d3ob01827j |
| 58. | Dharaniyedath, J.; Kumar, V.; Gandeepan, P. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 27, e202400649. doi:10.1002/ejoc.202400649 |
| 59. | Banerjee, S.; De, P. B.; Pradhan, S.; Shah, T. A.; Punniyamurthy, T. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2019, 1677–1684. doi:10.1002/ejoc.201801829 |
| 60. | Qiu, R.; Reddy, V. P.; Iwasaki, T.; Kambe, N. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 80, 367–374. doi:10.1021/jo502402d |
| 61. | De, P. B.; Banerjee, S.; Pradhan, S.; Punniyamurthy, T. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2018, 16, 5889–5898. doi:10.1039/c8ob01603h |
| 25. | Liu, Z.; Larock, R. C. Tetrahedron 2007, 63, 347–355. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2006.10.071 |
| 26. | Kitawaki, T.; Hayashi, Y.; Ueno, A.; Chida, N. Tetrahedron 2006, 62, 6792–6801. doi:10.1016/j.tet.2006.04.087 |
| 27. | Liu, Z.; Larock, R. C. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 3739–3741. doi:10.1021/ol048564l |
| 28. | Nozaki, K.; Takahashi, K.; Nakano, K.; Hiyama, T.; Tang, H.-Z.; Fujiki, M.; Yamaguchi, S.; Tamao, K. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2003, 42, 2051–2053. doi:10.1002/anie.200250648 |
| 62. | Santos, H.; Zeoly, L. A.; Rebechi, R.; Arantes, J.; Coelho, F.; Rodrigues, M. T., Jr. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2024, 366, 884–891. doi:10.1002/adsc.202301328 |
| 63. | Singh, S.; Samineni, R.; Pabbaraja, S.; Mehta, G. Org. Lett. 2019, 21, 3372–3376. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.9b01111 |
| 64. | Sinicropi, M. S.; Tavani, C.; Rosano, C.; Ceramella, J.; Iacopetta, D.; Barbarossa, A.; Bianchi, L.; Benzi, A.; Maccagno, M.; Ponassi, M.; Spinelli, D.; Petrillo, G. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 9139. doi:10.3390/app11199139 |
| 65. | Kim, M.; Jeon, S. K.; Hwang, S.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Yu, E.; Lee, J. Y. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 2485–2493. doi:10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b09114 |
| 66. | Fan, Z.; Ni, J.; Zhang, A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 8470–8475. doi:10.1021/jacs.6b03402 |
| 22. | Freeman, A. W.; Urvoy, M.; Criswell, M. E. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 70, 5014–5019. doi:10.1021/jo0503299 |
| 23. | Sanz, R.; Escribano, J.; Pedrosa, M. R.; Aguado, R.; Arnáiz, F. J. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2007, 349, 713–718. doi:10.1002/adsc.200600384 |
| 24. | Smitrovich, J. H.; Davies, I. W. Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 533–535. doi:10.1021/ol036294l |
| 20. | Kano, S.; Sugino, E.; Shibuya, S.; Hibino, S. J. Org. Chem. 1981, 46, 3856–3859. doi:10.1021/jo00332a019 |
| 21. | Hibino, S.; Tonari, A.; Choshi, T.; Sugino, E. Heterocycles 1993, 35, 441–444. doi:10.3987/com-92-s54 |
| 37. | Sinha, S. K.; Guin, S.; Maiti, S.; Biswas, J. P.; Porey, S.; Maiti, D. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 5682–5841. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.1c00220 |
| 38. | Rej, S.; Ano, Y.; Chatani, N. Chem. Rev. 2020, 120, 1788–1887. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00495 |
| 39. | Gandeepan, P.; Müller, T.; Zell, D.; Cera, G.; Warratz, S.; Ackermann, L. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 2192–2452. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00507 |
| 40. | Murakami, K.; Yamada, S.; Kaneda, T.; Itami, K. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 9302–9332. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00021 |
| 41. | Liu, C.-X.; Yin, S.-Y.; Zhao, F.; Yang, H.; Feng, Z.; Gu, Q.; You, S.-L. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 10079–10134. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00149 |
| 42. | Josephitis, C. M.; Nguyen, H. M. H.; McNally, A. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 7655–7691. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00881 |
| 43. | Docherty, J. H.; Lister, T. M.; Mcarthur, G.; Findlay, M. T.; Domingo-Legarda, P.; Kenyon, J.; Choudhary, S.; Larrosa, I. Chem. Rev. 2023, 123, 7692–7760. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00888 |
| 44. | Crabtree, R. H.; Lei, A. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 8481–8482. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00307 |
| 45. | Giri, R.; Shi, B.-F.; Engle, K. M.; Maugel, N.; Yu, J.-Q. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 3242–3272. doi:10.1039/b816707a |
| 46. | Wencel-Delord, J.; Dröge, T.; Liu, F.; Glorius, F. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4740–4761. doi:10.1039/c1cs15083a |
| 47. | Baudoin, O. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4902–4911. doi:10.1039/c1cs15058h |
© 2025 Kumar et al.; licensee Beilstein-Institut.
This is an open access article licensed under the terms of the Beilstein-Institut Open Access License Agreement (https://www.beilstein-journals.org/bjoc/terms), which is identical to the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0). The reuse of material under this license requires that the author(s), source and license are credited. Third-party material in this article could be subject to other licenses (typically indicated in the credit line), and in this case, users are required to obtain permission from the license holder to reuse the material.